What is marketing?
Marketing can be referred to as a form of communication with your customers, with the help of marketing tools such as advertising, promotion, publicity, design aspects related to the look of the product etc.
Marketing: Thinking global, teamwork, Global mind-set, Critical thinking and creativity
Marketing is about enjoying yourself, and pushing yourself to learn new skills. It’s where we, as the world’s leading body for marketers, can help you at each stage in your career through professional qualifications, membership and continuing professional development (CPD) that will not only give you a foothold in the marketing industry, but will also help you build a long and satisfying career within it.
*Advertising- In Advertising you will work with all aspects of marketing from strategy to concept to the execution of the strategy. You will find that most jobs on the business side of advertising include Account Management, Account Planners, and Media Buyers.
*Brand Management- Brand management is the career track you hear about most often. It is the key function in the consumer products industry. Brand managers are often likened to small business owners because they assume responsibility for a brand or brand family. They are always focused on the big picture. It is their job to distill the brand’s essence, map out their competitors in their brand’s category, identify marketing opportunities, and be able to effectively communicate the unique benefits of that product or service.
*Market Research- Market Research involves researching the intended target. That target can be companies or individuals. In order for a company to capture a market it must first be able to understand that market. Research involves the first process of understanding the consumer, what their needs are, what their purchasing habits are, and how they view themselves in relation to the rest of the world.
*Public Relations- It is the responsibility of the Public relations department to manage the communication with the media, consumers, employees, investors, and the general public. They are considered the spokespeople for the company. They will often write press releases to promote new products or to keep the investment community informed of business partnerships, financial results, or other company news
Marketing can be referred to as a form of communication with your customers, with the help of marketing tools such as advertising, promotion, publicity, design aspects related to the look of the product etc.
Marketing: Thinking global, teamwork, Global mind-set, Critical thinking and creativity
Marketing is about enjoying yourself, and pushing yourself to learn new skills. It’s where we, as the world’s leading body for marketers, can help you at each stage in your career through professional qualifications, membership and continuing professional development (CPD) that will not only give you a foothold in the marketing industry, but will also help you build a long and satisfying career within it.
*Advertising- In Advertising you will work with all aspects of marketing from strategy to concept to the execution of the strategy. You will find that most jobs on the business side of advertising include Account Management, Account Planners, and Media Buyers.
*Brand Management- Brand management is the career track you hear about most often. It is the key function in the consumer products industry. Brand managers are often likened to small business owners because they assume responsibility for a brand or brand family. They are always focused on the big picture. It is their job to distill the brand’s essence, map out their competitors in their brand’s category, identify marketing opportunities, and be able to effectively communicate the unique benefits of that product or service.
*Market Research- Market Research involves researching the intended target. That target can be companies or individuals. In order for a company to capture a market it must first be able to understand that market. Research involves the first process of understanding the consumer, what their needs are, what their purchasing habits are, and how they view themselves in relation to the rest of the world.
*Public Relations- It is the responsibility of the Public relations department to manage the communication with the media, consumers, employees, investors, and the general public. They are considered the spokespeople for the company. They will often write press releases to promote new products or to keep the investment community informed of business partnerships, financial results, or other company news
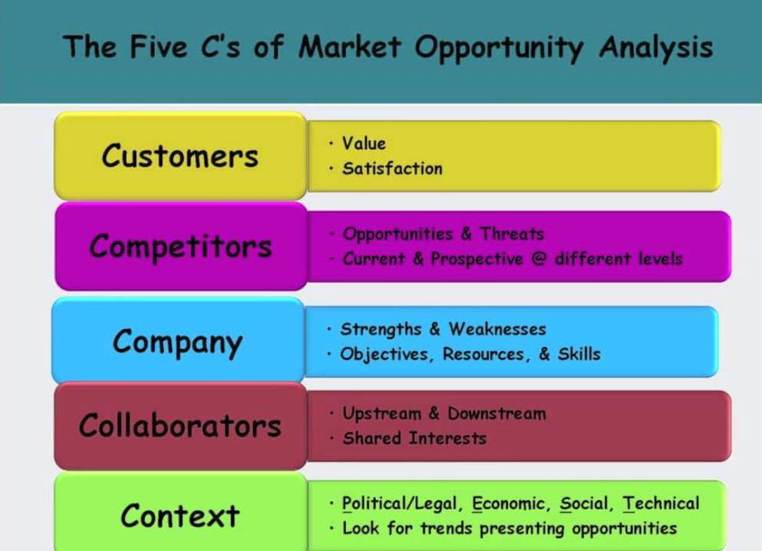
Definition: 5 C’s of Marketing
They are used to analyze the five key areas that are involved in marketing decisions for a company and include: Company, Customers, Competitors, Collaborators, and Climate. The 5 C’s are a good guideline to make the right decisions, and construct a well-defined marketing plan and strategy.
1. Customer – Determine what are the needs and from which clients that you’re trying to satisfy. A few areas of research can be market segments, frequency of purchases, quantity of purchases, retail channel, and customer needs depending on trends over time.
2. Company – Determine if your company is in a position to meet those customer needs. for example, whether your company has the right product line and technical expertise. A good tool to find out your company’s strengths and weaknesses is
“SWOT” analysis.
• Strengths: innovative products, expertise and procedures
• Weaknesses: lack of knowledgeable technical support or average product quality
• Opportunities: a new international market or a market led by a weak competitor
• Threats: a new competitor or price war
3. Competition – Determine who competes with your company in meeting the customer’s needs. Is the competitor an active competitor or is it a potential threat? What are their products exactly? What are their strengths and weaknesses?
4. Collaborators – Determine if there is any outside source or third party help that can help the company such as distributors, suppliers etc.
5. Context/Climate – Determine if there are any limitations due to
• Political issues: legal problems, trade regulations, taxes or labor laws
• Economic issues: growth rate, labor costs, and business cycle stage
• Social impacts: demographics, education, and culture
• Technological developments: impact on cost structures This is also known as “PEST” analysis.
They are used to analyze the five key areas that are involved in marketing decisions for a company and include: Company, Customers, Competitors, Collaborators, and Climate. The 5 C’s are a good guideline to make the right decisions, and construct a well-defined marketing plan and strategy.
1. Customer – Determine what are the needs and from which clients that you’re trying to satisfy. A few areas of research can be market segments, frequency of purchases, quantity of purchases, retail channel, and customer needs depending on trends over time.
2. Company – Determine if your company is in a position to meet those customer needs. for example, whether your company has the right product line and technical expertise. A good tool to find out your company’s strengths and weaknesses is
“SWOT” analysis.
• Strengths: innovative products, expertise and procedures
• Weaknesses: lack of knowledgeable technical support or average product quality
• Opportunities: a new international market or a market led by a weak competitor
• Threats: a new competitor or price war
3. Competition – Determine who competes with your company in meeting the customer’s needs. Is the competitor an active competitor or is it a potential threat? What are their products exactly? What are their strengths and weaknesses?
4. Collaborators – Determine if there is any outside source or third party help that can help the company such as distributors, suppliers etc.
5. Context/Climate – Determine if there are any limitations due to
• Political issues: legal problems, trade regulations, taxes or labor laws
• Economic issues: growth rate, labor costs, and business cycle stage
• Social impacts: demographics, education, and culture
• Technological developments: impact on cost structures This is also known as “PEST” analysis.
5 W’s of Marketing
1. WHY: The crucial first step
-> Firstly, ask yourself why you want to do a piece of marketing? This will give you your objective. Example: "I want to sell more cakes than bread".
-> Without this first step, you won't have a clear goal to work towards.
2. WHAT: The things that make your business unique
-> Now that you know why, you need to focus on what is unique about your business. Is there something specific that makes you stand out from the rest? The answer will give you your 'unique selling proposition' (USP). Example: Are you the guesthouse that accepts pets? The hair salon with the best shampoo massage?
-> Your USP is what makes your business different and unique to customers.
Tip: It helps to chat to your employees, friends or customers. They may bring insight from a different angle.
3. WHO: Get to know your customer
-> How well do you know your customers? In order to effectively speak to them, you need to know what they want and who they are. Example: Do you run a small sandwich delivery business in a busy office district?
-> Think about what busy office workers might need and when they might need it. - Get to understand when the staff at these offices go on lunch and what their preferences are. The better you know your customer, the better you can deliver a message or service to them.
Tip: Instead of asking your customers what they would like to see, ask your customers what they haven't seen yet. This simple change in perspective could bring ideas you haven't thought of yourself.
4. WHERE: the spots to find your customers
-> Once you know whom you want to talk to, think about where you will find these customers. Example: It could be a virtual place (Facebook) or physical place (the gym).
-> Think of unusual places that your competitors might not have considered such as Twitter. Example: If you run a spice shop, Twitter's character limit of 140 characters is perfect for tweeting spice-mix recipes.
5. WHEN: Timing is essential
-> Consider which calendar dates/events you can leverage. Example: When everyone is talking about a major sporting event and you run a related offer, people will associate your brand with the good feelings they have about a particular event.
-> 'When' is also about making the time to do your marketing and setting aside time to talk your customers.
6. HOW: Get your message out there
-> Now it's time to decide which methods will be right for you, and the quickest, most cost effective route is to look at online opportunities. Example: If your business relies heavily on visuals to sell, like a bakery would do, consider opening an Instagram account to post appealing daily specials.
-> The beauty of online? You can test what works first before you devote a big budget to your marketing efforts. Changes are easier, quicker and cheaper to make than with a printed flyer, for example.
1. WHY: The crucial first step
-> Firstly, ask yourself why you want to do a piece of marketing? This will give you your objective. Example: "I want to sell more cakes than bread".
-> Without this first step, you won't have a clear goal to work towards.
2. WHAT: The things that make your business unique
-> Now that you know why, you need to focus on what is unique about your business. Is there something specific that makes you stand out from the rest? The answer will give you your 'unique selling proposition' (USP). Example: Are you the guesthouse that accepts pets? The hair salon with the best shampoo massage?
-> Your USP is what makes your business different and unique to customers.
Tip: It helps to chat to your employees, friends or customers. They may bring insight from a different angle.
3. WHO: Get to know your customer
-> How well do you know your customers? In order to effectively speak to them, you need to know what they want and who they are. Example: Do you run a small sandwich delivery business in a busy office district?
-> Think about what busy office workers might need and when they might need it. - Get to understand when the staff at these offices go on lunch and what their preferences are. The better you know your customer, the better you can deliver a message or service to them.
Tip: Instead of asking your customers what they would like to see, ask your customers what they haven't seen yet. This simple change in perspective could bring ideas you haven't thought of yourself.
4. WHERE: the spots to find your customers
-> Once you know whom you want to talk to, think about where you will find these customers. Example: It could be a virtual place (Facebook) or physical place (the gym).
-> Think of unusual places that your competitors might not have considered such as Twitter. Example: If you run a spice shop, Twitter's character limit of 140 characters is perfect for tweeting spice-mix recipes.
5. WHEN: Timing is essential
-> Consider which calendar dates/events you can leverage. Example: When everyone is talking about a major sporting event and you run a related offer, people will associate your brand with the good feelings they have about a particular event.
-> 'When' is also about making the time to do your marketing and setting aside time to talk your customers.
6. HOW: Get your message out there
-> Now it's time to decide which methods will be right for you, and the quickest, most cost effective route is to look at online opportunities. Example: If your business relies heavily on visuals to sell, like a bakery would do, consider opening an Instagram account to post appealing daily specials.
-> The beauty of online? You can test what works first before you devote a big budget to your marketing efforts. Changes are easier, quicker and cheaper to make than with a printed flyer, for example.
Q-1) What is marketing?
Ans.
There are many good definitions of marketing available everywhere so you need to choose your effective one and prepare for that to discuss in interview, in case. Some are as follows:
-> Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably.
-> Marketing is communicating the value of a product, service or brand to customers, for the purpose of promoting or selling that product, service, or brand.
-> The management process through which goods and services move from concept to the customer.
-> The activities of a company associated with buying and selling a product or service. It includes advertising, selling and delivering products to people.
Q-2) What is the most interesting thing about marketing and sales?
Ans.
The most important and interesting thing you need to know about marketing and sales is that both activities are easy and fun.
*Marketing is a fun, creative activity. A lot of it, as you will see, is brainstorming around your cause and the people whom you hope to influence.
*Sales is also a fun activity, believe it or not. Okay perhaps not if you’re really shy, in which case you might want to stick with behind the scenes marketing or other activities. But many people, once they know what they’re doing and get in some practice, find that they like sales.
Q-3) What is the difference between marketing and selling?
Ans.
This is the most common question asked in every marketing interview. So the differences are: *Selling begins when a product or service becomes available for consumption or use.
This function covers retailers’ awareness and confidence on the product and cultivating customer advocacy for the maker of the product or service. *Marketing, on the other hand, is much broader in scope and starts long before the selling process takes place. It covers everything about the market, the consumer, and the brand.
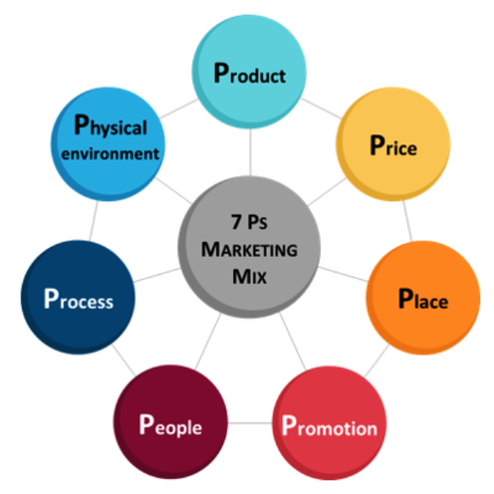
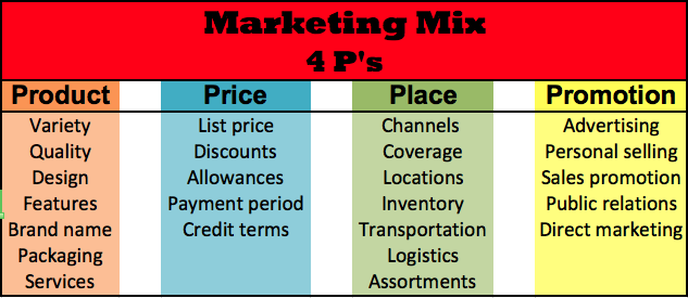
Q4) Tell me something about 4p’s of marketing.
Ans. The following describes the four P’s of marketing:
1) Product Products are the goods and services that your business provides for sale to your target market. When developing a product you should consider quality, design, features, money dollars covering costs expenses packaging, customer service and any subsequent after-sales service.
2) Place Place is in regards to distribution, location and methods of getting the product to the customer. This includes the location of your business, shop front, distributors, logistics and the potential use of the internet to sell products directly to consumers.
3) Price Price concerns the amount of money that customers must pay in order to purchase your products. There are a number of considerations in relation to price including price setting, discounting, credit and cash purchases as well as credit collection.
4) Promotion Promotion refers to the act of communicating the benefits and value of your product to consumers. It then involves persuading general consumers to become customers of your business using methods such as advertising, direct marketing, personal selling and sales promotion.
The extended 7 P’s:
5) People – All companies are reliant on the people who run them from front line Sales staff to the Managing Director. Having the right people is essential because they are as much a part of your business offering as the products/services you are offering.
6) Processes – The delivery of your service is usually done with the customer present so how the service is delivered is once again part of what the consumer is paying for.
7) Physical Evidence – Almost all services include some physical elements even if the bulk of what the consumer is paying for is intangible.
Ans.
There are many good definitions of marketing available everywhere so you need to choose your effective one and prepare for that to discuss in interview, in case. Some are as follows:
-> Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably.
-> Marketing is communicating the value of a product, service or brand to customers, for the purpose of promoting or selling that product, service, or brand.
-> The management process through which goods and services move from concept to the customer.
-> The activities of a company associated with buying and selling a product or service. It includes advertising, selling and delivering products to people.
Q-2) What is the most interesting thing about marketing and sales?
Ans.
The most important and interesting thing you need to know about marketing and sales is that both activities are easy and fun.
*Marketing is a fun, creative activity. A lot of it, as you will see, is brainstorming around your cause and the people whom you hope to influence.
*Sales is also a fun activity, believe it or not. Okay perhaps not if you’re really shy, in which case you might want to stick with behind the scenes marketing or other activities. But many people, once they know what they’re doing and get in some practice, find that they like sales.
Q-3) What is the difference between marketing and selling?
Ans.
This is the most common question asked in every marketing interview. So the differences are: *Selling begins when a product or service becomes available for consumption or use.
This function covers retailers’ awareness and confidence on the product and cultivating customer advocacy for the maker of the product or service. *Marketing, on the other hand, is much broader in scope and starts long before the selling process takes place. It covers everything about the market, the consumer, and the brand.
Q4) Tell me something about 4p’s of marketing.
Ans. The following describes the four P’s of marketing:
1) Product Products are the goods and services that your business provides for sale to your target market. When developing a product you should consider quality, design, features, money dollars covering costs expenses packaging, customer service and any subsequent after-sales service.
2) Place Place is in regards to distribution, location and methods of getting the product to the customer. This includes the location of your business, shop front, distributors, logistics and the potential use of the internet to sell products directly to consumers.
3) Price Price concerns the amount of money that customers must pay in order to purchase your products. There are a number of considerations in relation to price including price setting, discounting, credit and cash purchases as well as credit collection.
4) Promotion Promotion refers to the act of communicating the benefits and value of your product to consumers. It then involves persuading general consumers to become customers of your business using methods such as advertising, direct marketing, personal selling and sales promotion.
The extended 7 P’s:
5) People – All companies are reliant on the people who run them from front line Sales staff to the Managing Director. Having the right people is essential because they are as much a part of your business offering as the products/services you are offering.
6) Processes – The delivery of your service is usually done with the customer present so how the service is delivered is once again part of what the consumer is paying for.
7) Physical Evidence – Almost all services include some physical elements even if the bulk of what the consumer is paying for is intangible.
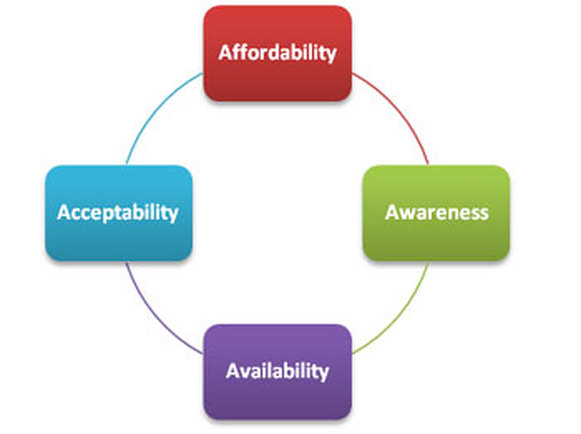
Components of the 4A Model
Acceptability - The Acceptability component of the 4A model says that a product or service must meet or exceed the needs and expectations of customers in a given target market. Acceptability has two dimensions - functional acceptability, and psychological acceptability. Functional acceptability refers to the "objective" performance attributes of a product or service. Does the product have the features that customers in the target market expect? Is it reliable? Does it perform as expected?
Psychological acceptability refers to the more "subjective" attributes of a product or service. We often see psychological acceptability associated with so-called "luxury" brands. So, for example, a mid-priced automobile may be as objectively functional as a vehicle of comparable size made by Mercedes or BMW. But those brands are more psychologically acceptable to a certain segment of buyers.
Affordability - Affordability refers to whether customers in the target market are able and willing to pay a product's price. As this definition indicates, affordability also has two dimensions - economic affordability and psychological affordability.
Economic affordability refers to whether the potential customers in the target market have sufficient economic resources to pay a product's price. Psychological affordability refers to a customer's willingness to pay, which is primarily determined by the customer's perception of the value he or she will obtain from a product or service relative to the cost of the product or service.
Accessibility - The third component of the 4A model is Accessibility, which describes whether customers can easily acquire and use a product or service. The two dimensions of accessibility are availability and convenience.
Availability measures whether a selling company has enough of a product to match customer demand. Convenience refers to how easy it is for potential customers to acquire a product or service. Robert Woodruff, the former chairman of Coca-Cola, captures the essence of Accessibility when he said in 1923 that Coca-Cola should always be "within an arm's length of desire."
Awareness - The final component of the 4A model is Awareness, which refers to whether customers are adequately informed about a product's attributes and benefits in a way that persuades potential buyers to give the product a try and reminds existing users whey they should continue to purchase a product. The two dimensions of Awareness are product knowledge and brand awareness. The basic idea here is that most potential customers will not buy unless they have a positive perception of the brand and adequate information regarding the specific product or service.
Acceptability - The Acceptability component of the 4A model says that a product or service must meet or exceed the needs and expectations of customers in a given target market. Acceptability has two dimensions - functional acceptability, and psychological acceptability. Functional acceptability refers to the "objective" performance attributes of a product or service. Does the product have the features that customers in the target market expect? Is it reliable? Does it perform as expected?
Psychological acceptability refers to the more "subjective" attributes of a product or service. We often see psychological acceptability associated with so-called "luxury" brands. So, for example, a mid-priced automobile may be as objectively functional as a vehicle of comparable size made by Mercedes or BMW. But those brands are more psychologically acceptable to a certain segment of buyers.
Affordability - Affordability refers to whether customers in the target market are able and willing to pay a product's price. As this definition indicates, affordability also has two dimensions - economic affordability and psychological affordability.
Economic affordability refers to whether the potential customers in the target market have sufficient economic resources to pay a product's price. Psychological affordability refers to a customer's willingness to pay, which is primarily determined by the customer's perception of the value he or she will obtain from a product or service relative to the cost of the product or service.
Accessibility - The third component of the 4A model is Accessibility, which describes whether customers can easily acquire and use a product or service. The two dimensions of accessibility are availability and convenience.
Availability measures whether a selling company has enough of a product to match customer demand. Convenience refers to how easy it is for potential customers to acquire a product or service. Robert Woodruff, the former chairman of Coca-Cola, captures the essence of Accessibility when he said in 1923 that Coca-Cola should always be "within an arm's length of desire."
Awareness - The final component of the 4A model is Awareness, which refers to whether customers are adequately informed about a product's attributes and benefits in a way that persuades potential buyers to give the product a try and reminds existing users whey they should continue to purchase a product. The two dimensions of Awareness are product knowledge and brand awareness. The basic idea here is that most potential customers will not buy unless they have a positive perception of the brand and adequate information regarding the specific product or service.
Q-5) Tell me something about PLC (Product life cycle).
Ans.
The product life cycle has 4 very clearly defined stages, each with its own characteristics that mean different things for business.
*INTRODUCTION In the Introduction stage of the product life cycle, a product or a service is introduced to the market. Consumers are testing the product in this phase.
*GROWTH After a product is introduced in the market, consumers become more interested in it. This is called the Growth stage of the product life cycle. Sales are increasing and competitors are emerging as well. Products become more profitable and companies form alliances, joint ventures, and takeovers.
*MATURITY The market has reached saturation. Some producers at a later stage of the Maturity stage of the product life cycle begin to leave the market due to poor profit margins. Sales dynamics is Vishal Thakur 6 beginning to decrease.
*DECLINE Continuous decline in sales signals entry into the Decline stage of the production life cycle. Competition is taking over your market share at this point. Economic and production conditions are becoming unfavourable.
Q-6) For a new salesperson, what are his needs?
Ans.
New salespersons needs:
* He needs to know the information on company history, its policies, rules and regulations etc.
*Details about the product- its features, usage , demand.
*Systems and procedures as followed by the company.
This may include the work timings, overtime, field work, work culture of that particular organisation etc.
*Training on the basic ethics that need to be followed while selling a product.
*He must know the basics of selling the different products of the company.
Q-7) Why do you want to work in marketing field?
Ans.
The best way to answer this question is, first of all, to be prepared and knowledgeable about this field. Spend some time researching the marketing field so you can talk about the benefits of working in this area. Compare your goals, let the interviewer know what best you can do in marketing job even though the question is about why you want to work here, you still need to convince the interviewer that hiring you will benefit the company.
Q-8) What are the keys to marketing success?
Ans.
The keys to marketing success are:
*Budgeting.
*Targeting.
*Analyzing the Competition.
*Working Your Customer Base.
*Development of Objectives.
Q-9) What motivates you?
Ans.
Here the interviewer is trying to understand the key to your being successful in the job he is interviewing for, and wants to make sure it’s a good fit. So consider, in advance of interviewing, what actually does motivate you and come up with some specific examples
Q-10) Are you competitive by nature?
Ans.
Competition is very important to survive in the market so to achieve success in this field you have to be competitive. Suite the examples of your work related to market competition in your answer as proof .
Q-11) Why Is Online Marketing So Effective?
Ans.
Online marketing is also known as web marketing, internet marketing, eMarketing or imarketing. Online marketing is an interactive tool which can be used between marketers and the public at large. Online marketing is so effective because:
*Online marketing allows for statistics to be measured more easily and at a lower cost.
*Online marketing costs are somewhat inexpensive in comparison with other mediums.
*Online marketing allows consumers of the world to research and purchase services and products at their own pace and convenience.
*Online marketing provides a greater flexibility level whereby campaigns can be altered to test new markets, evaluate new programmes and make changes more specific to a targeted market.
Q-12) Do me a favour, Sell this pen to me.
Ans.
The key point of this question is to see if you understand what selling is all about. 9 out of 10 people will immediately start describing the pen and its features (like people did during the seminar at the end of the movie) – “it writes smoothly”, “it looks great”, “it’s cheap”, etc. This is an indication that they are clueless about selling. A correct approach is to first investigate client’s needs by asking questions about their situation, then address those needs with the product capabilities in a way that creates clear and significant value in their minds, and then convert this value into cash. That is the point of the test: to see if you can discover the needs, develop a solution, and close the deal.
Q-13) Do you consider yourself a leader?
Ans.
You might think that leadership questions are only relevant for management positions, but that’s a common misconception. Most companies are looking for people with leadership potential even when hiring for entry-level positions. So be prepared in advance for this question. I recommend that every job seeker prepare at least one example of a leadership experience with a strong reason that why you consider yourself leader and get comfortable speaking about it in an interview situation.
Q-14) What makes a successful marketing manager?
Ans.
To be a successful marketing manager you must :
*Have the effective sales skills.
*Fill your work with passion.
*Master the corporate balancing act.
*Understand your domains.
*Enough experience to understand what a given project may typically cost, is able to prepare a budget.
Q-15) Tell me something about your previous marketing experience?
Ans. Previous work experience is the basis for determining whether you will be a valuable contributor to an organization. If you are fresher show experience of marketing college events n festivals. For this reason, applicants must present their previous experience in a way that emphasizes how it will specifically and significantly benefit the college. So share your past but good experience with your interviewer and what and how much you have learned there.
Q-16) What is the most important skill required in marketing field?
Ans.
The most important skills required in marketing are:
*Risk-taking.
*Know your audience.
*Be a good listener.
*Be open to new ideas.
*Be accurate but nimble.
*Know what the competition is doing.
*Passion: Love marketing.
*Experimentation: Try something new.
*Fail. Try again.
*Communication: Articulate your point of view well via speaking and writing
Ans.
The product life cycle has 4 very clearly defined stages, each with its own characteristics that mean different things for business.
*INTRODUCTION In the Introduction stage of the product life cycle, a product or a service is introduced to the market. Consumers are testing the product in this phase.
*GROWTH After a product is introduced in the market, consumers become more interested in it. This is called the Growth stage of the product life cycle. Sales are increasing and competitors are emerging as well. Products become more profitable and companies form alliances, joint ventures, and takeovers.
*MATURITY The market has reached saturation. Some producers at a later stage of the Maturity stage of the product life cycle begin to leave the market due to poor profit margins. Sales dynamics is Vishal Thakur 6 beginning to decrease.
*DECLINE Continuous decline in sales signals entry into the Decline stage of the production life cycle. Competition is taking over your market share at this point. Economic and production conditions are becoming unfavourable.
Q-6) For a new salesperson, what are his needs?
Ans.
New salespersons needs:
* He needs to know the information on company history, its policies, rules and regulations etc.
*Details about the product- its features, usage , demand.
*Systems and procedures as followed by the company.
This may include the work timings, overtime, field work, work culture of that particular organisation etc.
*Training on the basic ethics that need to be followed while selling a product.
*He must know the basics of selling the different products of the company.
Q-7) Why do you want to work in marketing field?
Ans.
The best way to answer this question is, first of all, to be prepared and knowledgeable about this field. Spend some time researching the marketing field so you can talk about the benefits of working in this area. Compare your goals, let the interviewer know what best you can do in marketing job even though the question is about why you want to work here, you still need to convince the interviewer that hiring you will benefit the company.
Q-8) What are the keys to marketing success?
Ans.
The keys to marketing success are:
*Budgeting.
*Targeting.
*Analyzing the Competition.
*Working Your Customer Base.
*Development of Objectives.
Q-9) What motivates you?
Ans.
Here the interviewer is trying to understand the key to your being successful in the job he is interviewing for, and wants to make sure it’s a good fit. So consider, in advance of interviewing, what actually does motivate you and come up with some specific examples
Q-10) Are you competitive by nature?
Ans.
Competition is very important to survive in the market so to achieve success in this field you have to be competitive. Suite the examples of your work related to market competition in your answer as proof .
Q-11) Why Is Online Marketing So Effective?
Ans.
Online marketing is also known as web marketing, internet marketing, eMarketing or imarketing. Online marketing is an interactive tool which can be used between marketers and the public at large. Online marketing is so effective because:
*Online marketing allows for statistics to be measured more easily and at a lower cost.
*Online marketing costs are somewhat inexpensive in comparison with other mediums.
*Online marketing allows consumers of the world to research and purchase services and products at their own pace and convenience.
*Online marketing provides a greater flexibility level whereby campaigns can be altered to test new markets, evaluate new programmes and make changes more specific to a targeted market.
Q-12) Do me a favour, Sell this pen to me.
Ans.
The key point of this question is to see if you understand what selling is all about. 9 out of 10 people will immediately start describing the pen and its features (like people did during the seminar at the end of the movie) – “it writes smoothly”, “it looks great”, “it’s cheap”, etc. This is an indication that they are clueless about selling. A correct approach is to first investigate client’s needs by asking questions about their situation, then address those needs with the product capabilities in a way that creates clear and significant value in their minds, and then convert this value into cash. That is the point of the test: to see if you can discover the needs, develop a solution, and close the deal.
Q-13) Do you consider yourself a leader?
Ans.
You might think that leadership questions are only relevant for management positions, but that’s a common misconception. Most companies are looking for people with leadership potential even when hiring for entry-level positions. So be prepared in advance for this question. I recommend that every job seeker prepare at least one example of a leadership experience with a strong reason that why you consider yourself leader and get comfortable speaking about it in an interview situation.
Q-14) What makes a successful marketing manager?
Ans.
To be a successful marketing manager you must :
*Have the effective sales skills.
*Fill your work with passion.
*Master the corporate balancing act.
*Understand your domains.
*Enough experience to understand what a given project may typically cost, is able to prepare a budget.
Q-15) Tell me something about your previous marketing experience?
Ans. Previous work experience is the basis for determining whether you will be a valuable contributor to an organization. If you are fresher show experience of marketing college events n festivals. For this reason, applicants must present their previous experience in a way that emphasizes how it will specifically and significantly benefit the college. So share your past but good experience with your interviewer and what and how much you have learned there.
Q-16) What is the most important skill required in marketing field?
Ans.
The most important skills required in marketing are:
*Risk-taking.
*Know your audience.
*Be a good listener.
*Be open to new ideas.
*Be accurate but nimble.
*Know what the competition is doing.
*Passion: Love marketing.
*Experimentation: Try something new.
*Fail. Try again.
*Communication: Articulate your point of view well via speaking and writing
Marketo
Marketo is a web service that provides tools for managing marketing campaigns. It is provided by Marketo, SaaS revenue performance management company specializing in marketing automation and sales effectiveness software for mid-size and enterprise business-to-business (B2B) companies.
Hubspot
HubSpot provides tools for social media marketing, content management, web analytics, landing pages and search engine optimization.
The HubSpot suite of online tools has three primary applications:
1) Content management tools for creating or managing blogs, templates, forms and landing pages;
2) Exposure optimization applications that help the content be found, such as through search engine optimization;
3) Lead tracking and intelligence tools, which track and manage e-mail marketing, customer interactions, qualified prospects, reports and analysis.
Marketo is a web service that provides tools for managing marketing campaigns. It is provided by Marketo, SaaS revenue performance management company specializing in marketing automation and sales effectiveness software for mid-size and enterprise business-to-business (B2B) companies.
Hubspot
HubSpot provides tools for social media marketing, content management, web analytics, landing pages and search engine optimization.
The HubSpot suite of online tools has three primary applications:
1) Content management tools for creating or managing blogs, templates, forms and landing pages;
2) Exposure optimization applications that help the content be found, such as through search engine optimization;
3) Lead tracking and intelligence tools, which track and manage e-mail marketing, customer interactions, qualified prospects, reports and analysis.